What is the Dark Web and how does it work?
- over 1 year ago
- 5 min read
You probably have heard of the term “Dark Web” before. And although the Dark Web may seem like something out of a mystery novel, it is real and is a big part of the internet. Let's look at what it is, how it works, and how it differs from conventional web.
The Dark Web is the internet's hidden alleyways, tucked away from the bustling streets of the World Wide Web that most of us are familiar with. Unlike the websites you visit every day, the Dark Web is inaccessible via standard web browsers or indexed by traditional search engines, such as Google.
Dark Web, Deep Web, Surface Web
The internet most people know about can be broadly divided into three distinct segments or levels: the Surface Web, the Deep Web, and the Dark Web. The Surface Web and Deep Web account for 94% of all the information on the internet, while the Dark Web is estimated to account for around 6%.
The Surface Web, also known as Clearnet or the visible web, is the portion of the internet that is readily accessible to the general public and is indexed by traditional search engines. When you search for a recipe, read news articles, or visit social media platforms, you are navigating the Surface Web.
The Deep Web is a much bigger part of the internet, but standard search engines do not index it. This includes databases, private academic libraries, member-only websites, and personal email accounts. You are accessing the Deep Web when you log into your online banking account to check your balance or view transactions. While the term 'Deep Web' might sound mysterious, it’s largely unnoticeable, encompassing content that’s not intended for access without the appropriate authorization or credentials.
The Surface Web and Deep Web account for 94% of all the information on the internet, while the Dark Web is estimated to account for around 6%.
The hidden internet
Lastly, there's the Dark Web, a small and deliberately hidden part of the internet that is not accessible through regular browsers. It requires special software, such as Tor or I2P, to access it. The Dark Web is notorious for its illegal activities. Although it’s true that illicit activities are prevalent on the Dark Web, it is also a platform where political dissidents can engage in communication in countries with oppressive regimes, or where whistleblowers can divulge information without fear of reprisal.
The origins and rise of the Dark Web
The roots of the Dark Web can be traced back to the 1990s, when the U.S. Naval Research Laboratory initiated a project called 'onion routing', a technique for anonymous communication over a computer network. This project ultimately led to the creation of Tor in the mid-2000s.
The primary objective of Tor was to safeguard the online communications of U.S. intelligence. However, once it was released to the public, the broader community began to recognize its potential for ensuring privacy and resisting censorship. As internet use increased, people started to worry about privacy, surveillance and censorship, which led to Tor becoming more popular.
By the 2010s, with the emergence of marketplaces like Silk Road, the Dark Web started to gain notoriety as a hub for illicit activities. Although these marketplaces brought attention and controversy to the Dark Web, they also ignited the broader debate regarding internet freedom, privacy, and the challenges of digital governance.
How The Onion Router works
Until you see how Tor works, the onion in the Tor name might seem like an odd choice. The onion represents the concept of working in layers. All traffic in Tor is relayed and encrypted three times as it travels over the Tor network. The data is passed through several of the thousands of Tor relays. There’s no single relay that knows where the data originally came from or where it is going. You can compare it to passing a secret note through a group of people, with each person adding a new layer of code to keep the message hidden.
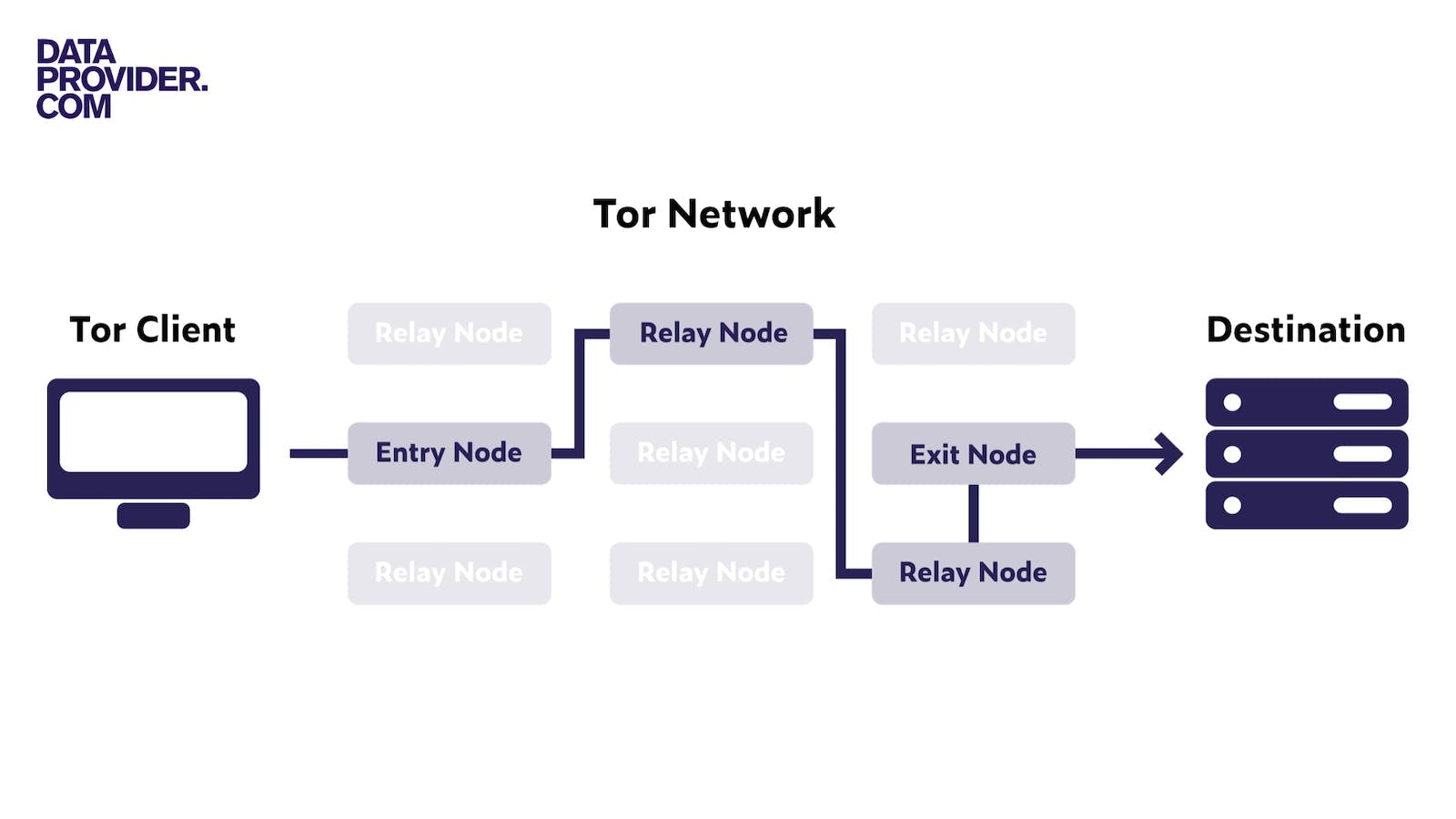
With Tor, internet traffic is routed and encrypted multiple times, which makes it difficult to track activities or locations. Despite Tor's association with accessing the hidden parts of the internet, such as the Dark Web, it can also be used for regular browsing.
Privacy on the Dark Web: The good & the bad
The concept of privacy is a fundamental characteristic of the Dark Web, and it is one of the primary reasons why individuals and organizations may choose to operate there. The Dark Web is distinguished from other parts of the internet by its unique combination of secrecy, anonymity and association with both legal and illegal activities. The illegal aspect of the Dark Web often prevails when people are referring to it. The origin for that negative sentiment can partly be found in the marketplaces on the Dark Web.
Marketplaces for illegal activities
Marketplaces are places that facilitate trade and communication in a shielded environment. Users can buy, sell and exchange goods and services with a heightened sense of anonymity. Common illegal goods and services on offer include, for example, illicit drugs, stolen data, malware and hacking services, firearms and counterfeit identity documents or money. In 2022, you could buy valid US credit card information for as little as $17 or a New York driver's license for around $70.
Some marketplaces have gained notoriety, the most notable of which being AlphaBay and Silk Road. Silk Road, which debuted in 2011, was a pioneer in the underground digital bazaar scene, offering a diverse range of products, ranging from illicit drugs to counterfeit currency. Its user-friendly interface and reliance on Bitcoin as an anonymous payment method made it a massive hit among Dark Web users. However, its prominence also made it a prime target for law enforcement, leading to its eventual closure in 2013.
The dark side of the Dark Web
AlphaBay quickly filled the void left behind by Silk Road and expanded the range of illicit activity. These marketplaces, while providing a glimpse into the Dark Web's hidden economy, also highlight the seemingly endless cat-and-mouse game between cybercriminals and global law enforcement agencies. AlphaBay was shut down in 2017 by law enforcement.
In 2021 it was relaunched. But at the beginning of 2023, the owner seemingly disappeared. Due to the way security was set up, the site was basically rendered unusable and it died a slow death. That Illicit activity is lucrative is not a surprise. A prime example of that is Hydra. In 2022, that marketplace was shut down by German and U.S. authorities. At that time, it was the highest-grossing Dark Web marketplace, with an estimated revenue of €1.23 billion.
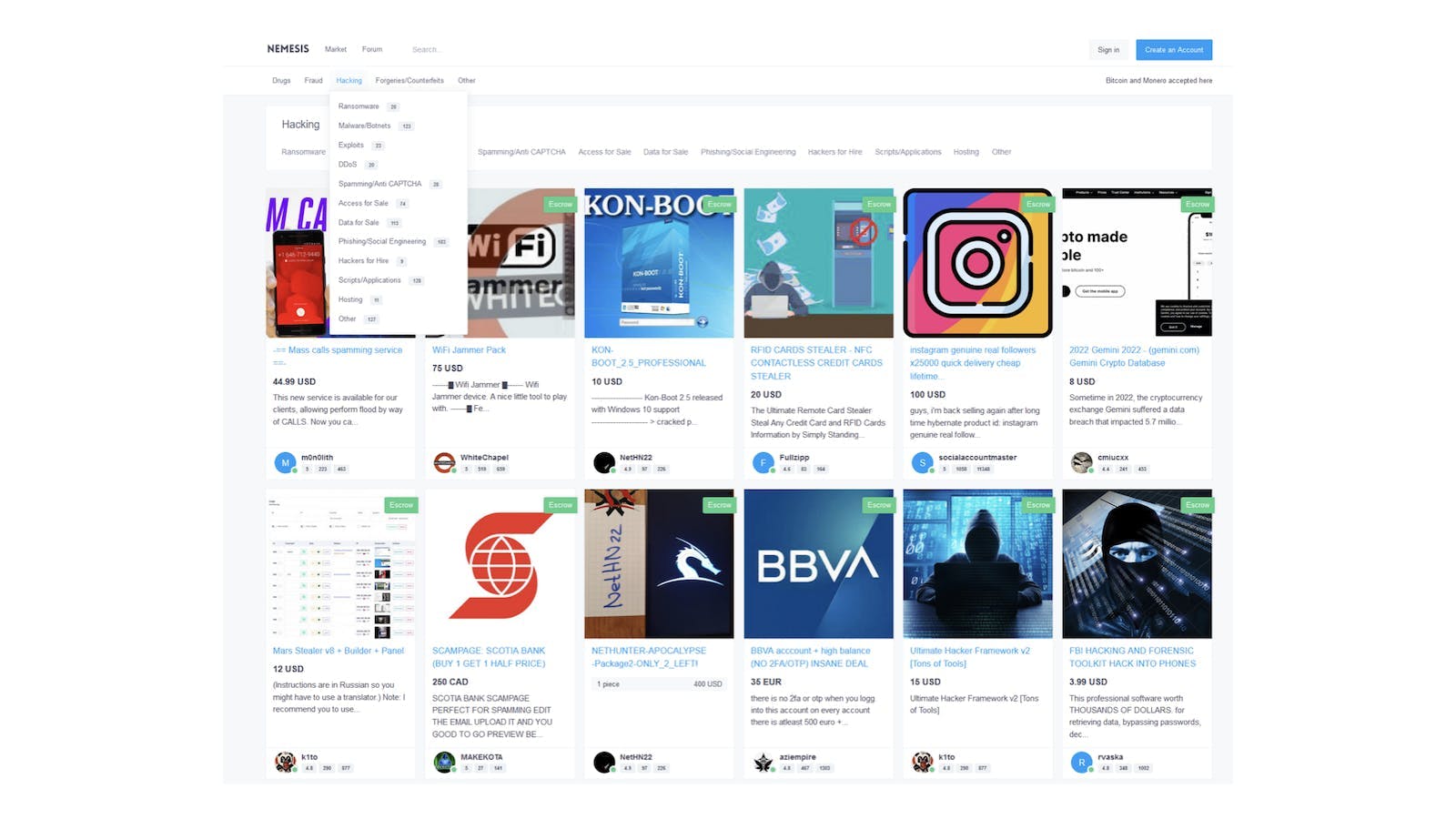
The light side of the Dark Web
The Dark Web is rife with illicit activities and potential dangers, but it also serves as a sanctuary for whistleblowers and those evading political repression. Nevertheless, its reputation is primarily shaped by the trade in illegal goods, services and stolen data. It's important to recognize the dual nature of the Dark Web and remain vigilant about personal and organizational cybersecurity measures. To safeguard against data leaks and the potential dissemination of sensitive information on the Dark Web, businesses should adopt comprehensive cybersecurity strategies.